There is a specific way to format content for AI search engines that improve your chance of being cited.
AI systems extract and process content differently than humans. To optimize your content for SEO for AI tools like ChatGPT or Perplexity, you need to focus on clear, modular formatting. This involves writing self-contained sections, using concise language, and structuring information with headings, bullet points, and tables when necessary. Here’s what you need to know:
- AI extracts content in chunks (200–400 words) and relies on headings, lists, and tables to identify key points.
- Short, standalone sections improve accuracy and reduce errors when AI systems retrieve information.
- Use question-based headings and direct answers to align with user queries.
- Avoid vague pronouns like “it” or “this” to ensure clarity when content is read in isolation.
- Structured formats, like tables and lists, increase the likelihood of AI citation by 28–40%.
- Keep paragraphs brief (2–5 sentences) and write at an 8th–11th-grade reading level.
Quick Tips for AI-Friendly Content:
- Start with the answer: Use the BLUF (Bottom Line Up Front) method to summarize key points in the first few sentences.
- Use clear headings: Organize content with logical H2 and H3 tags that match common search queries.
- Write concise paragraphs: Stick to one idea per paragraph for better AI processing.
- Leverage lists and tables: Use these sparingly to highlight comparisons or structured data.
- Update content regularly: AI tools prioritize citations from recently updated pages.
By following these steps, your content becomes easier for AI systems to process, making it more likely to be cited in AI-generated responses. This approach not only improves visibility but also positions your content as a trusted source for decision-makers using AI tools.
How AI Systems Extract and Process Content
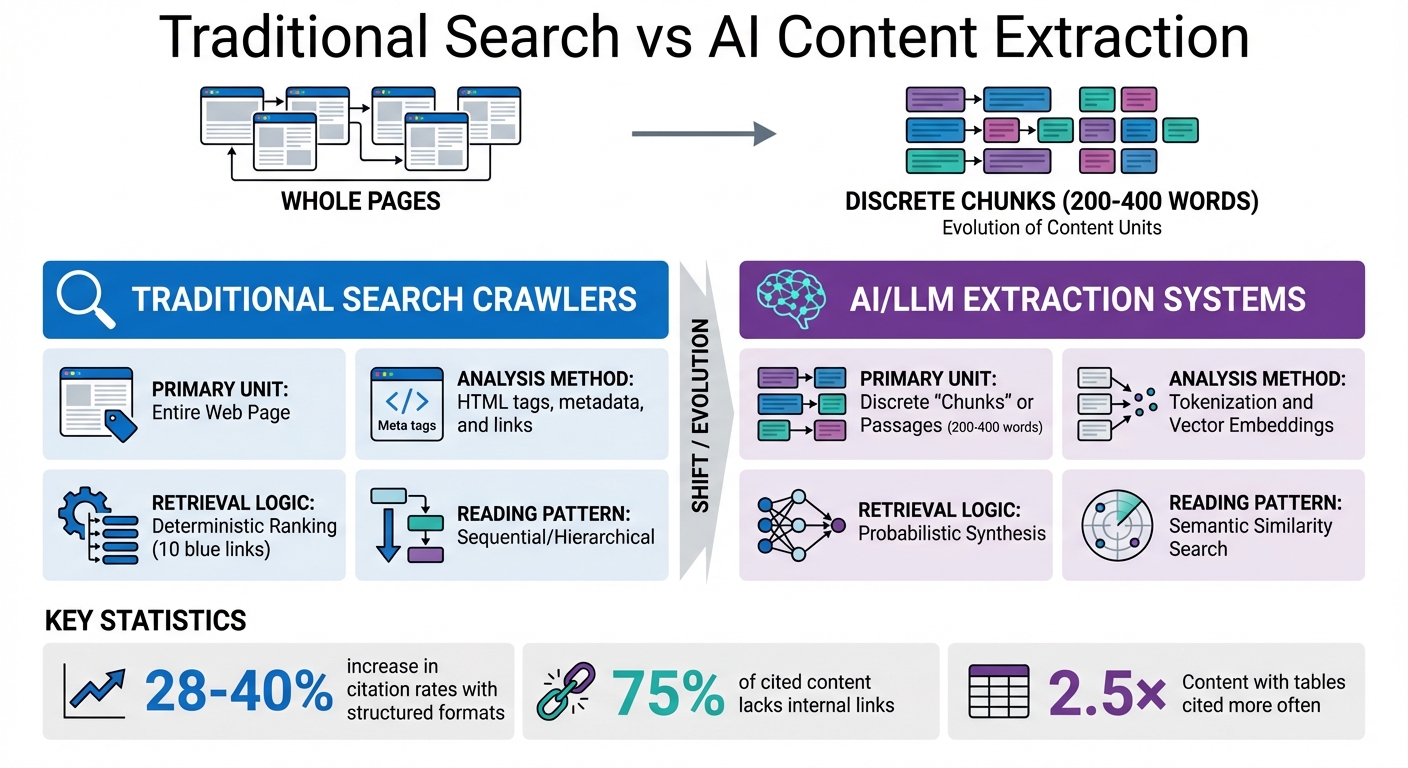
Traditional Search vs AI Content Extraction: Key Differences
AI systems don’t process content the way humans read – line by line or paragraph by paragraph. Instead, they rely on a Retrieval-Augmented Generation (RAG) pipeline, which breaks articles into smaller, manageable “chunks.” These chunks typically range from 200 to 1,000 tokens, or roughly 200–400 words. Each chunk is indexed separately in vector databases. This allows the AI to retrieve only the most relevant pieces when answering a query [7][1]. For instance, if a user asks a question, the system performs a similarity search across these indexed chunks. It then pulls the most relevant passages and combines them into a cohesive response [7][2]. This means that even in a long article, only a few key chunks are retrieved to address the query. That’s why crafting concise, standalone sections is so critical.
This process also reveals a key limitation: traditional narrative writing doesn’t always work well for AI systems. Content that relies on transitional phrases or vague pronouns can lose meaning when taken out of context, making it harder for the AI to interpret or cite effectively [1]. This is where concise, self-contained passages shine.
Why AI Prefers Short, Standalone Passages
AI models follow a U-shaped attention pattern – they focus most on the beginning and end of a document or chunk, while paying less attention to the middle [8]. This is why the BLUF method (Bottom Line Up Front) is so effective. Starting each section with a brief, clear summary of 2–4 sentences makes it more likely that the content will be cited.
Short, standalone passages also help reduce the chances of AI “hallucinations”, where the system generates incorrect or misleading information. When the content is modular and straightforward, the AI can synthesize responses more accurately without needing to infer missing context [3][9]. This modular design improves efficiency, enabling the AI to retrieve and process information quickly and precisely.
Additionally, research shows that structured formats like headings, bullet points, and Q&A blocks increase citation rates by 28–40% for large language models (LLMs) [5]. In a study analyzing over 2,200 AI Overview citations, 75% of cited content lacked internal links, indicating that AI systems favor clean, uncluttered text chunks [1].
How Structure and Clear Language Help AI
Given the importance of discrete chunks, clear formatting and structure play a crucial role in AI extraction. Elements like headings, paragraph breaks, and lists act as “semantic flags” that help the AI understand where one idea ends and another begins [1][5]. For example, a clear H2 or H3 heading signals the start of a new topic, which aids in accurate indexing. Without these markers, the AI might split the content incorrectly, leading to confusion or loss of meaning.
Using question-based headings can also be highly effective. A heading like “How do AI systems process text?” is far more aligned with user search behavior than something generic like “Content Strategy” [1][5]. This alignment increases the chances that the content will be selected when responding to a query.
Equally important is the use of clear, simple language. Writing at an 8th- to 11th-grade reading level makes content easier for AI systems to understand and cite [3]. Avoid vague pronouns at the start of paragraphs. Instead, repeat specific nouns (e.g., “Vector search” instead of “It”) to ensure each chunk remains meaningful when retrieved in isolation [1][4]. Unlike traditional SEO, which relies on backlinks and metadata, AI models prioritize structure and clarity [5].
Here’s a quick comparison to highlight the differences in how traditional search engines and AI systems process content:
| Feature | Traditional Search Crawlers | AI/LLM Extraction Systems |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Unit | Entire Web Page | Discrete “Chunks” or Passages [8][7] |
| Analysis Method | HTML tags, metadata, and links | Tokenization and Vector Embeddings [3][7] |
| Retrieval Logic | Deterministic Ranking (10 blue links) | Probabilistic Synthesis [3] |
| Reading Pattern | Sequential/Hierarchical | Semantic Similarity Search [7][2] |
Understanding this shift in content processing helps lay the groundwork for creating content optimized for AI. Up next, we’ll dive into specific formatting techniques to ensure your content is AI-friendly and ready for extraction.
How to Format Content for AI Extraction
AI thrives on well-structured, modular content. By formatting your content into clear sections with defined boundaries, you make it easier for AI to extract and interpret information. Here’s how to do it effectively.
Write Clear Headings with Proper Hierarchy
Headings act as signposts, showing where topics begin and end. Using proper H1–H6 tags in a logical sequence helps AI understand the importance of each section and how ideas are connected. For example, question-based H2 headings like “How do you format content for AI?” are more effective than vague titles like “Our Approach.” These headings align with common search queries, making them both user- and AI-friendly.
Follow H2 headings with H3 subheadings that provide direct answers or address specific subtopics. This structure allows AI to extract individual sections as standalone answers without relying on the rest of the page for context. Always maintain a strict hierarchy (H1 > H2 > H3) without skipping levels, and avoid quirky or branded headings like “Our Secret Sauce.” Instead, opt for descriptive, keyword-focused titles like “AI Extraction Best Practices.” For more foundational advice, see our guide to writing for SEO optimization.
After each heading, include a concise summary of 40–60 words to outline the main idea. Ensure the accompanying text is brief, focused, and self-contained for easy extraction.
Keep Paragraphs Short and Sentences Simple
AI systems process content in chunks, typically 200–400 words per section. To avoid confusion, keep paragraphs between 2–5 sentences (75–150 words). Shorter paragraphs ensure clarity and prevent ideas from being split mid-thought. Use straightforward, active voice sentences. For example, “An HRIS manages payroll” is clearer than “Payroll is managed by an HRIS.”
Avoid jargon and stick to plain English. Use specific nouns rather than vague pronouns like “it” or “this” to keep each paragraph understandable when read independently. Front-load the most important details in the first few sentences, and avoid transitional phrases like “Furthermore” or “Additionally” unless you re-establish context. Each section should stand alone without relying on prior paragraphs.
Use Bullets, Tables, and Text Formatting
Bullets and tables are excellent tools for creating clear, extractable content boundaries. Tables, in particular, make data relationships explicit, reducing the AI’s interpretation workload. In fact, content with tables is cited 2.5× more often than unstructured text [6].
When using bullet points, maintain a consistent structure. For instance, if one bullet begins with a verb, all should follow suit. Limit lists to 3–7 items for readability, and always provide a brief introduction before presenting a list or table to frame the information.
Highlight important terms or definitions with bold text to create semantic signals that help AI identify key concepts. Use native HTML elements like <ul>, <ol>, and <table> instead of styled <div> tags. Semantic HTML provides clear structural cues to crawlers, making your content easier for AI to process.
“LLMs extract information through pattern matching. Numbered lists create clear extraction boundaries. Tables provide explicit data relationships. Both reduce the AI’s interpretation work and increase citation confidence.” – Onely [6]
sbb-itb-16c0a3c
Before-and-After Formatting Examples
Understanding how narrative content can be reshaped into a more structured format helps illustrate the benefits clearly. Below, you’ll find two examples that show how reformatting content can make it more accessible for AI systems.
Example 1: Turning Narrative Text into Structured Content
Before (Narrative Format):
“When selecting a project management tool, consider key factors such as pricing, features, and integrations. Evaluate pricing models – per user versus flat monthly rates. Then there are the features – does it have task tracking, reporting, and collaboration tools? And don’t forget about integrations with the software you already use, like Slack or Google Workspace. It’s a difficult decision that requires careful evaluation of your team’s specific needs.”
This long block of text makes it hard to extract key points and lacks a clear structure.
After (Structured Format):
How Do You Choose the Right Project Management Tool?
To select the right project management tool, focus on pricing, features, and integrations that align with your team’s needs. A structured format like this uses a question-based heading and concise points to improve clarity.
Key factors to evaluate:
- Pricing: Compare flat monthly rates with per-user pricing models.
- Features: Look for task tracking, reporting, and collaboration capabilities.
- Integrations: Ensure compatibility with tools like Slack and Google Workspace.
This approach not only makes the content easier to read but also helps AI systems extract essential insights more effectively.
Example 2: Using Tables for Data Comparisons
Building on structured text, tables take it a step further by presenting information in a clear, side-by-side format.
Before (Paragraph Format):
“Traditional SEO focuses on improving search rankings through keyword optimization and backlinking, while GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) aims to optimize for AI citation by using modular, extractable content. SEO often relies on tools like Ahrefs for keyword research, whereas GEO requires prompt testing to see how AI retrieves information.”
This format makes it harder to compare the two approaches at a glance.
After (Table Format):
| Feature | Traditional SEO | GEO (Generative Engine Optimization) |
|---|---|---|
| Primary Goal | Rank in Google search results | Get cited in AI-generated answers |
| Content Format | Keyword-optimized pages | Modular, extractable sections |
| Key Tools | Ahrefs, backlink analysis | Prompt testing |
Tables make it easy to compare data and highlight differences. This clarity improves how AI systems process and cite information, reducing ambiguity.
Both examples show how strategic formatting – whether through bullet points or tables – can transform content into digestible and extractable sections, enhancing its usability for both readers and AI systems.
How RankWriters Improves AI Citations
RankWriters combines proven formatting techniques with targeted strategies to make content more discoverable by AI tools. The platform emphasizes two key approaches: AI Search Optimization and pillar content strategies. Together, these methods enhance the chances that AI systems like ChatGPT, Perplexity, and Google’s AI Overviews will recognize and cite your business as a reliable source. These strategies build on modular formatting principles, refining your content to maximize its citation potential.
RankWriters’ AI Search Optimization Methods
RankWriters employs atomic content strategies, ensuring each section provides a self-contained, complete answer. This is achieved through a “Bottom Line Up Front” (BLUF) approach, where direct, concise answers (40–60 words) appear at the start of each section [8][6]. This format allows AI models to extract information quickly, avoiding unnecessary introductory text.
Headings are crafted using H2 and H3 tags that mimic natural language queries, such as “How do you choose a project management tool?” This signals relevance to AI systems searching for specific answers [2][5]. Additionally, clear and straightforward language ensures that each section remains meaningful, even when viewed in isolation [10][1].
The platform’s research and keyword strategies focus on creating “source content” that is both factually dense and precise – qualities AI systems prioritize when selecting citations [10]. Structured content, such as tables and data, is particularly effective; research shows that content with tables is cited 2.5 times more often than unstructured text, and articles exceeding 2,000 words are 3 times more likely to earn citations than shorter pieces [6].
Building Content Pillars for More AI Citations
RankWriters also strengthens authority through comprehensive content pillars. These pillars act as in-depth “ultimate guides” on broad topics, supported by detailed subtopic articles. AI systems favor this interconnected body of work over standalone articles when evaluating citation-worthiness [2]. While pillar pages establish overall authority, the more specific, deeply nested cluster pages are often the ones cited, as they provide the precise details AI systems seek [6].
The platform enhances these connections through descriptive internal linking, using keyword-rich anchor text to highlight topical relationships and signal relevance to AI models [2][5]. This topic cluster approach helps AI systems map the depth of your site’s content, making individual pages within a cluster more likely to be cited. Notably, 82.5% of AI citations link to specific, topic-focused pages rather than a homepage [6].
To maintain relevance, RankWriters updates content every 30 days, refreshing statistics, examples, and timestamps. This aligns with AI citation engines’ preference for current information – 76.4% of the most-cited pages by ChatGPT were updated within the past 30 days [6].
Conclusion: Main Points for AI-Friendly Formatting
Let’s recap the key strategies for creating content that drives results and is optimized for AI systems.
AI tools process content in chunks, so each section needs to stand on its own. To achieve this, use answer-first formatting – put the direct answer in the first 40–60 words. Pair this with question-based headings that reflect natural queries, and keep paragraphs short (2–5 sentences) while focusing on a single idea. Structured formats like tables and lists are especially useful, with tables being highly effective for increasing citation rates [6]. Also, avoid vague pronouns like “it” or “this” at the start of sentences; instead, use specific nouns to keep the content clear and self-contained. Since AI models often prioritize the beginning and end of sections (a U-shaped attention bias), leading with your main point is crucial for visibility [8].
“The winning approach isn’t trying to game the pipeline. It’s creating clear, self-contained sections that deliver complete answers.” – Despina Gavoyannis, Senior SEO Specialist, Ahrefs [8]
RankWriters applies these strategies to maximize AI extraction and citation. The platform ensures every section is self-contained, uses answer-first formatting for clarity, and refreshes content every 30 days to stay relevant. This aligns with findings that 76.4% of the most-cited pages were updated within the past month [6]. These tactics not only improve AI citations but also attract highly engaged, intent-driven visitors. By following these principles, your content remains clear, authoritative, and ready for AI-driven platforms.
FAQs
How does AI extract and process content differently from traditional search engines?
AI systems operate by pinpointing specific, self-contained sections of content that directly answer a query, rather than scanning through an entire page from start to finish. Unlike traditional search engines, which depend on link-based rankings and full-page indexing, AI zeroes in on intent-driven retrieval, identifying the most relevant bits of information.
Because of this, it’s crucial to structure content in a way that’s easy for AI to extract. Clear headings, short paragraphs, and bullet points help ensure that key information is quickly accessible and ready to meet user needs.
Do question-based headings make content AI-friendly?
Yes, question-based headings do make content AI-friendly.
Question-based headings are a smart way to match your content with the questions people are actually asking. They make it easier for AI systems to locate and pull out the most relevant information. Plus, these headings break your content into clear, focused sections that AI tools can process individually, boosting the chances that your work gets cited or referenced by AI-powered platforms.
This approach not only makes your content more useful for AI but also improves how it connects with human readers, increasing both engagement and visibility.
Why is it important to format content into modular sections for AI citation?
Breaking your content into clear, self-contained sections makes it easier for AI systems to pull out specific details. Instead of processing an entire article, AI tools often work with smaller pieces of information.
To optimize for this, use concise headings, short paragraphs, and bullet points where it makes sense. This structure not only boosts the chances of your content being accurately cited by AI but also ensures your message is delivered clearly and with authority.